In today's rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, efficiency, precision, and power density are paramount. Gear motors play a crucial role in achieving these objectives across a wide range of applications, from robotics and automation to electric vehicles and industrial machinery. Understanding how to select and calculate the correct gear motor is no longer a niche engineering concern; it's a pivotal factor in optimizing production processes and achieving cost-effectiveness. This article delves into the key selection points and calculation methods from a manufacturing perspective, highlighting the importance of leveraging technological advancements and considering emerging trends like Industry 4.0 and the push for sustainable manufacturing. MES-Drive is a leading provider of gear motor solutions, and this article will utilize their expertise and insights.
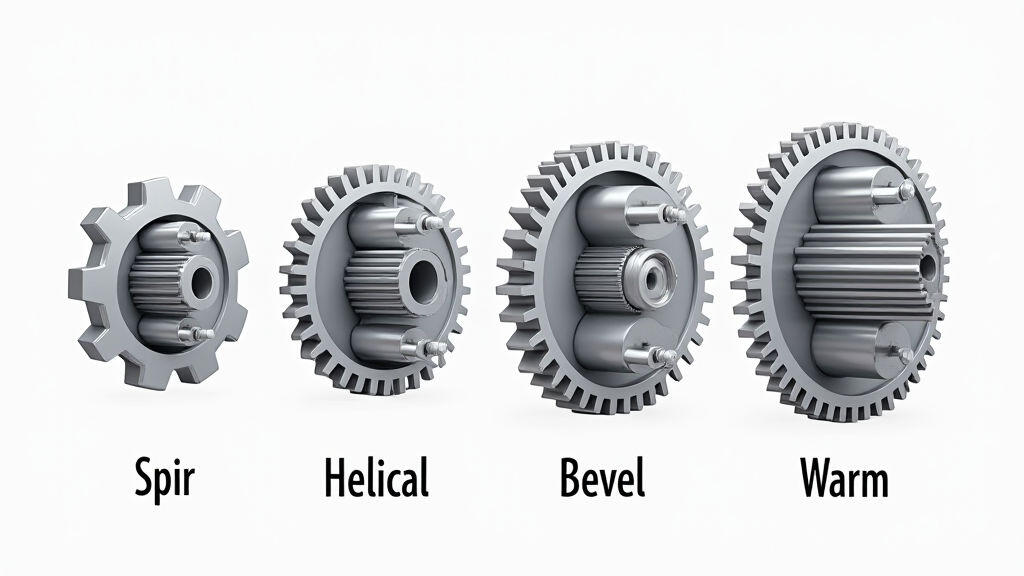
At its core, a gear motor combines a motor with a gearbox to deliver a desired speed and torque output. The motor provides the rotational power, while the gearbox modifies this power to suit the specific needs of the application. Gear motors are broadly categorized into:
Choosing the right type is the first critical step. Factors influencing this choice include required torque, speed, efficiency, space constraints, and noise levels.

Selecting a gear motor isn't a simple equation. Manufacturing environments demand specific characteristics. Here's a breakdown of crucial selection points:
Torque Requirements: This is arguably the most important factor. Determine the required output torque based on the load the gear motor will be driving. Consider both static and dynamic loads. Over-sizing the motor is costly, while under-sizing will lead to premature failure. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) simulations are often used in modern manufacturing to accurately predict torque demands under various operating conditions.
Speed Requirements: Calculate the desired output speed. This is directly related to the required process speed and the mechanical characteristics of the driven equipment. Consider the motor's operating speed range and the gear ratio needed to achieve the desired output speed.
Efficiency: Energy consumption is a major concern. Higher efficiency translates to lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact. Look for gear motors with high efficiency ratings, particularly for applications with continuous operation. MES-Drive gear motors often incorporate advanced materials and optimized designs to maximize efficiency.
Accuracy & Precision: For applications requiring precise positioning (e.g., robotics, CNC machines), the gear motor’s accuracy is critical. Consider the backlash, which is the amount of play in the gear mesh. Low backlash gear motors are available, although they typically come at a higher cost.
Size & Weight: Space constraints are often a significant factor in manufacturing facilities. Select a gear motor that fits within the available space while meeting the torque and speed requirements. Weight is also important, particularly for mobile applications.
Environmental Conditions: Consider the operating environment – temperature, humidity, dust, and vibration. Choose a gear motor with appropriate protection ratings (IP rating) to ensure reliable operation in harsh conditions. Some gear motors are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, which is essential in demanding manufacturing processes.
Durability & Reliability: Gear motors need to withstand prolonged operation. Consider the material quality of the gears, bearings, and housing, as well as the overall construction of the motor. MES-Drive utilizes high-quality materials and rigorous testing procedures to ensure the durability and reliability of its products.
Accurate calculation methods are essential for selecting the right gear motor and ensuring optimal performance. Here are some key calculations:
Gear Ratio Calculation: The gear ratio (GR) is the ratio of the input speed to the output speed. It is calculated as: GR = Input Speed / Output Speed. This determines how much the speed is reduced by the gearbox.
Torque Calculation: The output torque is related to the input torque and the gear ratio by the following equation: Output Torque = Input Torque * Gear Ratio. This is fundamental to ensuring the motor can provide sufficient power to drive the load.
Efficiency Calculation: Efficiency is the ratio of output power to input power: Efficiency = (Output Power / Input Power) * 100%. This calculation involves considering the input power of the motor and the output power of the gearbox, taking into account any losses due to friction.
Backlash Calculation: For precision applications, calculating backlash is crucial. Backlash is the difference between the theoretical ideal of no play and the actual clearance between the meshing gear teeth. This measurement, often expressed in arcminutes or degrees, impacts positional accuracy..
Power Loss Calculation: Various power losses occur within a gearmotor, including friction losses, viscous losses, and electrical losses. Understanding these losses is critical for accurately predicting energy consumption and thermal management requirements.
The rise of Industry 4.0 is driving innovation in gear motor technology. Connectivity, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance are becoming increasingly important. Gear motors equipped with sensors can provide valuable data on performance, allowing for proactive maintenance and optimized operation.
MES-Drive is actively developing gear motors that integrate with IoT platforms, enabling remote monitoring and control. AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze sensor data to predict potential failures, reducing downtime and improving overall efficiency. Furthermore, lightweight, high-power density gear motors are essential for electric vehicle manufacturing and automation, aligning with trends towards sustainability.
The relentless pursuit of energy efficiency, precision, and connectivity in manufacturing demands innovative gear motor solutions. MES-Drive and other industry leaders are at the forefront of this revolution, developing solutions that meet the evolving needs of a connected, data-driven manufacturing world.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked