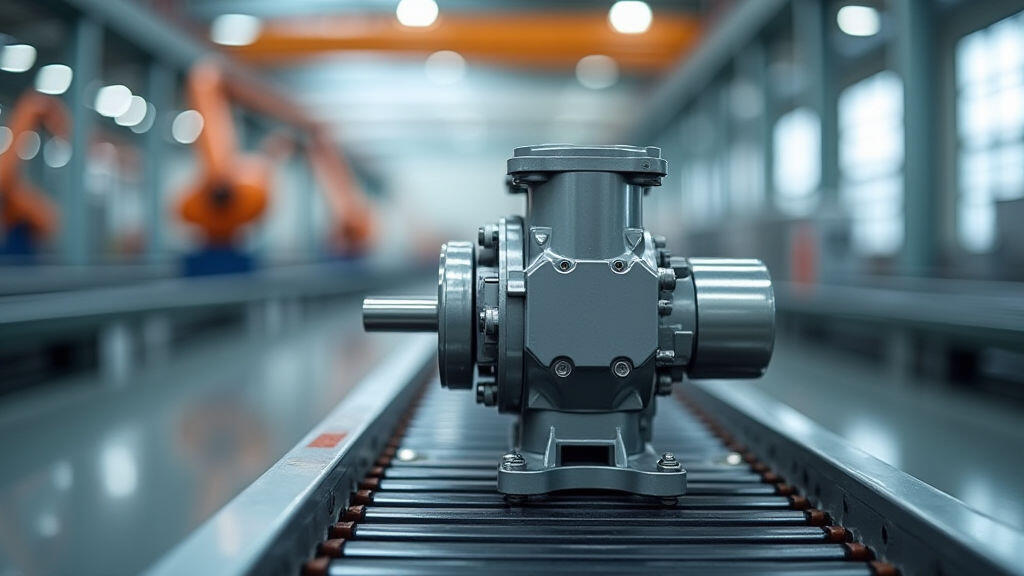
Modern agricultural factories are under pressure to produce more with less – faster output, lower operating costs, and reduced environmental impact. One overlooked hero in this push for progress is the right‑angle gear motor. By combining compact design with high torque transfer, these motors are turning the dial on speed and energy efficiency across the whole crop‑processing and equipment‑assembly chain.

Unlike conventional long shaft motors, a right‑angle gear motor uses a gear train to redirect the output shaft 90 degrees. The input shaft stays parallel to the motor housing, while the output shaft moves sideways. This configuration allows machinery to be built tighter together, eliminates awkward extensions, and keeps the center of gravity low. The gear system also locks up the motor, preventing slip and preserving power under load.
Speed is critical when processing grain, husking roots, or assembling parts. Right‑angle gear motors enable quick acceleration without bulky gearing. Their high torque per inch of shaft diameter means a single motor can drive a conveyor or turning table at a higher rpm than a conventional motor would need. The mechanical advantage of the gear train also smooths out start‑up spikes, giving workers a more predictable and safer operating environment. Because the motor’s shaft is perpendicular to its housing, technicians can mount the device in tight spaces and still access the drive side for maintenance, reducing downtime.

Energy consumption accounts for a significant portion of agricultural manufacturing costs. The compactness of right‑angle gear motors helps lower the motor’s internal friction. Their gear train is typically a single stage or a compact planetary arrangement, which reduces the number of moving parts that can wear and slip. The result? Less heat loss, less stray power draw, and a tighter duty cycle. Moreover, because they can operate at higher speeds, they often run at a more efficient point on the motor’s torque‑speed curve.
Beyond the motor itself, the straight‑line drive path simplifies belt routing or couplings, minimizing energy losses due to misalignment or tension. When matched with variable‑speed drives, the motor can be throttled precisely to match production needs, avoiding the waste of running at full power all the time.
Automated tractors, seed drill assemblers, and milling machines all can benefit from right‑angle gear motors. Installation is a matter of securing the motor’s lateral output to the driven component – whether it’s a rotating screw, a turning table, or a conveyor. Modern PLC (programmable logic controller) systems can easily control the motor’s start‑stop and speed cycles, making integration almost plug‑and‑play.
Because the output shaft is perpendicular, designers can route cables or hydraulic lines along the motor housing, providing a cleaner look and reducing the risk of wear on connectors. This layout is especially useful for vertical farms or greenhouse automation where space is at a premium.
1. **Silicon Valley Seed Co.** – By replacing a 1.5‑hp traditional motor with a 1‑hp right‑angle gear motor on their seed‑sorting line, they cut energy usage by 12% while boosting throughput by 18%.
2. **Midwestern Milling Facility** – Installation of dual right‑angle gear motors on the grain loader reduced conveyor wear by 30% and cut the average cycle time from 28 seconds to 22 seconds per batch.
3. **Agri‑Tech Start‑up** – In a prototype vertical farm, right‑angle gear motors powered their hydroponic tilters, allowing the tilting mechanism to operate in under a second, which improved the plant growth cycle by 5%.
As electric vehicles and sustainability move up the priority list, right‑angle gear motors are getting smarter. Companies are now embedding sensor suites that monitor vibration, temperature, and wear patterns in real time. This data feeds into predictive maintenance platforms, allowing farms to schedule repairs before a fault occurs, preserving uptime.
Materials science is also contributing: new ceramic gear teeth and lightweight alloys reduce weight while boosting wear resistance, further cutting energy usage. Coupled with variable‑frequency drives, the future right‑angle gear motor will operate at the minimal power needed for each task, almost eliminating idle energy draw.
Right‑angle gear motors may be small in size, but their impact on speed and energy efficiency is vast. By shifting power output perpendicular to the motor body, they enable tighter engine layouts, smoother operation, and fewer energy losses. Their scalability and ease of integration mean they can fit into anything from a seed‑drill assembler to a high‑speed grain conveyor. As sensor tech and materials innovation drive them further into the future, we can expect even greater gains in productivity and sustainability for agriculture’s production lines. Embracing this technology today positions manufacturers to meet tomorrow’s demanding standards for speed, cost, and environmental stewardship.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked