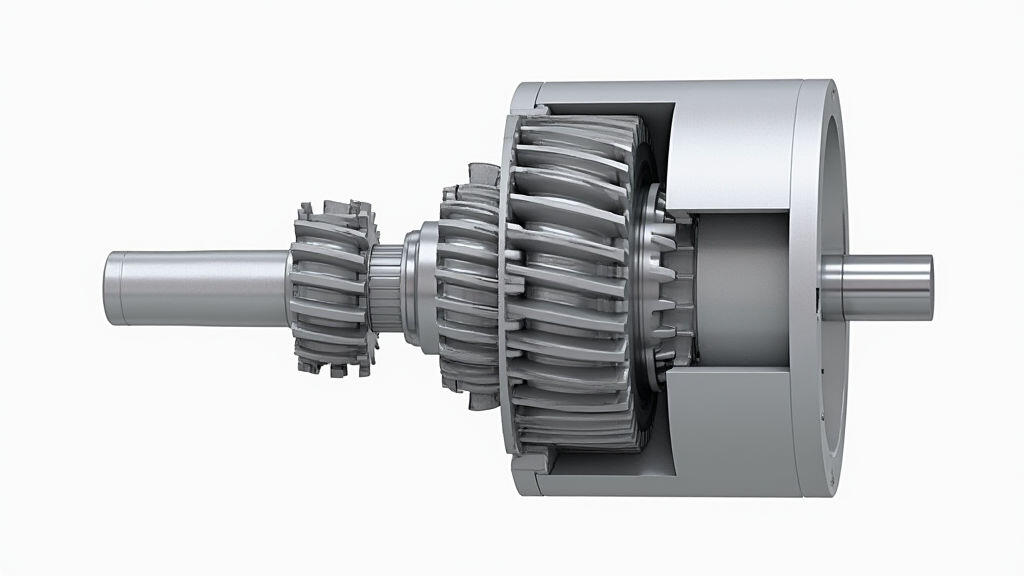
The relentless march of automation is transforming manufacturing processes globally. At the heart of many automated production lines lie gear motors – robust, efficient, and versatile power sources driving everything from conveyor belts to robotic arms. Understanding their principles, performance characteristics, and optimal applications is crucial for maximizing production efficiency, minimizing downtime, and remaining competitive in today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape. This article provides an in-depth analysis of gear motors, exploring their inner workings, performance metrics, and diverse applications, with a particular focus on their role in modern automated production lines. As we navigate the ongoing challenges of supply chain resilience and the increasing demand for agile manufacturing, the role of reliable and efficient gear motors has never been more critical.
A gear motor is essentially an electric motor coupled with a gear reducer. The electric motor provides rotational power, while the gear reducer modifies the speed and torque of that power. The core principle lies in the mathematical relationship between rotational speed and torque. By increasing the number of gear teeth in the gear reducer, the motor’s speed is reduced, and its torque is amplified. This allows for the delivery of higher torque at lower speeds, a critical requirement for many automated applications.
There are several types of gear motors, each with distinct characteristics and suitable for different purposes:

The efficiency of a gear motor is affected by several factors, including gear design, lubrication, and load conditions. Modern gear motors often incorporate advanced materials and manufacturing techniques to minimize friction and maximize efficiency.
When selecting a gear motor for an automated production line, several performance indicators warrant careful consideration:
Modern gear motors are often equipped with advanced sensors and control systems for monitoring performance and optimizing operation. Data analytics and predictive maintenance are becoming increasingly common, allowing for proactive identification of potential issues and minimizing downtime.
Gear motors are ubiquitous in automated production lines, powering a wide range of equipment and processes:
The rise of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) are further driving the adoption of smart gear motors. These smart motors are equipped with sensors and communication capabilities that allow them to connect to a network and share data. This enables remote monitoring, diagnostics, and control, leading to improved efficiency and predictive maintenance.
Recent global events have highlighted the vulnerability of complex supply chains. The reliance on geographically dispersed suppliers can lead to disruptions and delays. This has intensified the demand for more resilient and agile manufacturing processes. Gear motors, as essential components of automated production lines, must also be part of this resilience strategy.
MES-Drive, for example, is actively investing in diversifying its supply chain and developing partnerships with regional suppliers. They are also focusing on designing gear motors with modular components, making them easier to repair and maintain. Furthermore, MES-Drive provides comprehensive remote monitoring and diagnostics capabilities, allowing customers to proactively address potential issues and minimize downtime. The ability to quickly adapt to changing market demands and disruptions is paramount, and robust gear motors form the backbone of this adaptability.
The future of gear motors in automated production lines is bright. Several key trends are shaping the industry:
In conclusion, gear motors are indispensable components of modern automated production lines. Their ability to efficiently convert electrical energy into mechanical power, coupled with their versatility and robustness, makes them ideal for a wide range of applications. As manufacturers increasingly prioritize supply chain resilience and agility, the role of reliable and efficient gear motors will only become more critical. Companies like MES-Drive are leading the way in developing innovative gear motor solutions that address these challenges and enable manufacturers to thrive in the age of automation. The advancements in smart technology, materials science, and predictive maintenance promise a future where gear motors will play an even greater role in driving productivity, efficiency, and sustainability in the manufacturing sector.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked