
Last month, the Global Manufacturing Innovation Summit (GMIS) in Shenzhen drew more than 12,000 industry leaders, many of whom highlighted a single trend that is changing the face of production: the integration of Artificial Intelligence into real‑time machine control and predictive maintenance. The conference’s keynote speaker, Dr. Lin Zhao, called AI‑driven automation “the next industrial revolution’s backbone,” a statement that resonated across automotive plants, electronics assemblers, and even apparel manufacturers. This surge in AI adoption is not just a software upgrade; it requires equally sophisticated hardware capable of translating digital signals into precise, reliable motion. Enter the gear motor—formerly the unsung hero of factory automation—now stepping into the spotlight as a critical enabler of high‑performance, AI‑guided robotics and equipment.

At its core, a gear motor (or reducer motor) combines an electric motor with a gear train to provide high torque at low speeds. In the context of AI‑driven automation, these motors serve three pivotal roles:
During the GMIS panel discussion, several case studies illustrated this synergy:
Each example underscores how gear motors transform “thinking machines” into reliable, high‑performing tools. Their compactness and robustness make them ideal for AI‑controlled work cells where space constraints and power density are critical.
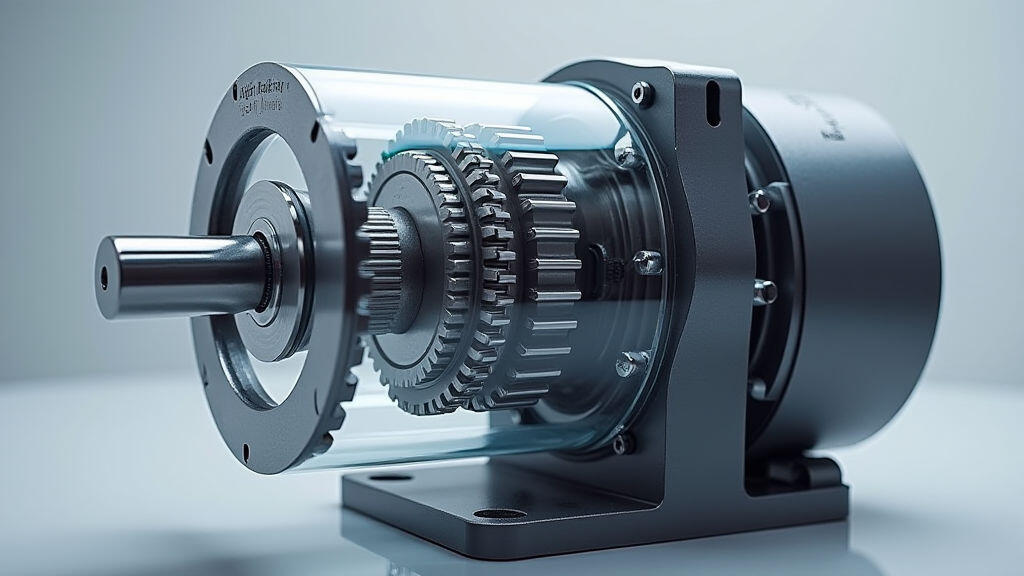
The trend towards AI and automation has squeezed the traditional gear motor market, but it has also accelerated it. Analysts from MarketsandMarkets project the global gear motor market to grow to $18 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5%. Key drivers include:
The next wave of innovation will see gear motors themselves become smarter. Modern drivers may integrate embedded microcontrollers and open communication protocols (like CAN‑FD or EtherCAT), allowing them to participate directly in distributed control systems. AI algorithms could then optimize motor operation in real time, adjusting torque profiles to balance speed, efficiency, and wear. Imagine a factory where every motor reports its health status to a central AI hub, which reallocates workload and steers production in milliseconds.
Moreover, the rise of edge AI—on‑device intelligence—could shift many control tasks from cloud servers to the motors themselves. This reduces latency, increases reliability, and empowers highly mobile robots to adapt instantly to dynamic environments—critical for applications like warehouse automation and last‑mile delivery.
In the age of AI‑driven automation, the gear motor is more than just a motor; it is a critical cog in the machinery of progress. Its ability to deliver precise torque, consume less energy, and provide actionable data aligns perfectly with the demands of intelligent factories. As the global manufacturing industry embraces intelligent control, data analytics, and sustainability, gear motors will remain indispensable—pulsing the lifeblood of AI‑enhanced production lines worldwide. The synergy between cutting‑edge software and robust hardware signals a promising future where human ingenuity is amplified by machines that not only move but also think, learn, and adapt.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked