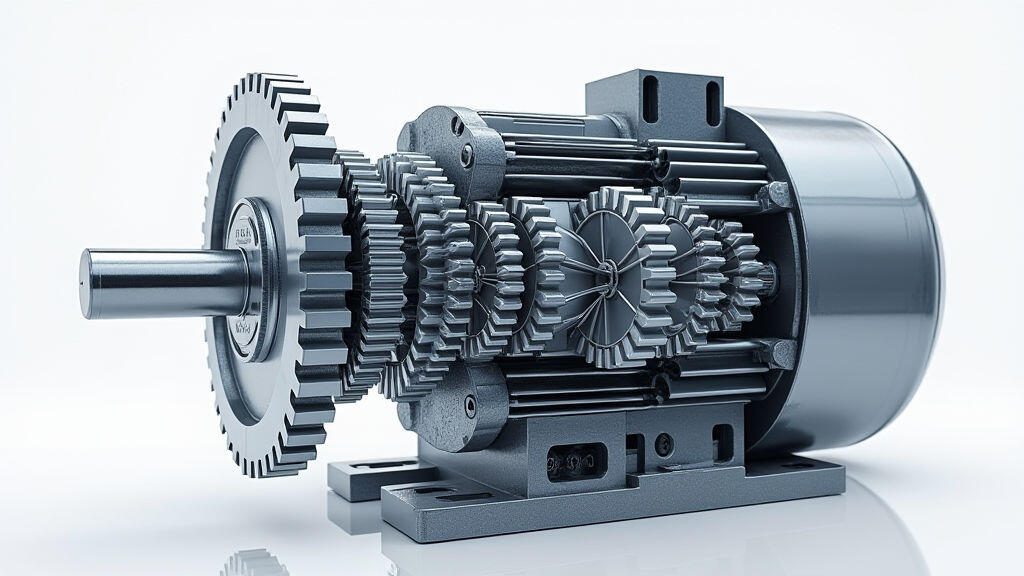
The agricultural sector is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by the need for increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, and sustainable practices. Automation is at the heart of this revolution, with increasingly sophisticated machinery capable of performing tasks from planting and harvesting to precision spraying and livestock management. A crucial component in these automated systems is the gear motor – the workhorse that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion with the precision and power needed for demanding agricultural applications. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to understanding gear motor principles and selecting the right one for your agricultural machinery upgrade, with a focus on ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. With the rise of AI-powered farming solutions and the increasing demand for smart agriculture, choosing the correct gear motor becomes even more critical.
Modern agriculture faces unprecedented challenges. A growing global population necessitates higher crop yields, while labor shortages and rising input costs put immense pressure on farmers. Automation offers a pathway to address these challenges. Automated tractors, robotic harvesters, and precision irrigation systems are becoming increasingly commonplace. These machines rely heavily on precise and reliable gear motors for tasks like controlling actuators, adjusting valve positions, and powering various mechanisms. Moreover, the trend toward data-driven farming, fueled by IoT sensors and AI, requires reliable and responsive machinery, further emphasizing the importance of efficient gear motor performance.
Gear motors are electromechanical devices that combine an electric motor with a gear reducer. This combination allows for significant changes in torque and speed. Let's break down the key principles:
Motor Types: The foundation of any gear motor is the electric motor. Common types include:
Gear Types and Their Characteristics: The gear reducer is what provides the torque amplification and speed reduction.
Gear Ratio: The gear ratio is the key parameter determining the output speed and torque. It's calculated by dividing the motor speed by the gear speed. A higher gear ratio results in lower output speed and higher torque, while a lower gear ratio results in higher output speed and lower torque. Selecting the correct gear ratio is paramount for optimizing machine performance.

Selecting the right gear motor isn't a one-size-fits-all process. It requires careful consideration of the specific application requirements. Here's a breakdown of common agricultural machinery applications and recommended gear motor characteristics:
Tractors: Tractors demand high torque at low speeds for plowing, tilling, and pulling implements. AC induction motors with high gear ratios (e.g., 10:1 to 30:1) are commonly used to provide the necessary power. Consider rugged, sealed gear motors designed to withstand harsh conditions and dust exposure.
Harvesters: Harvesting equipment involves a variety of tasks, including cutting, separating, and conveying crops. BLDC motors or AC induction motors with moderate gear ratios (e.g., 5:1 to 15:1) are often used to power these mechanisms. Reliability and efficiency are critical for maximizing harvesting yields and minimizing downtime.
Sprayers: Precision spraying requires accurate control of spray nozzles and pumps. DC motors with varying gear ratios (e.g., 2:1 to 10:1) are ideal for controlling pump speed and nozzle adjustment. Water resistance and durability are also important considerations.
Irrigation Systems: Variable frequency drives (VFDs) coupled with AC gear motors offer precise control over water flow rates. Gear ratios can range from 3:1 to 20:1, depending on the pump requirements. Energy efficiency is a key factor in minimizing operating costs.
Robotic Systems: Agricultural robotics are pushing the boundaries of automation. BLDC motors with high torque-to-weight ratios and precise speed control are commonly used in robotic arms and mobile platforms. Gear ratios can vary depending on the specific robotic application.
When upgrading agricultural machinery with gear motors, consider these crucial factors:
Operating Environment: Agricultural environments are often harsh, with exposure to dust, moisture, extreme temperatures, and vibrations. Choose gear motors with appropriate IP (Ingress Protection) ratings to ensure protection against these elements. Look for sealed and shielded designs.
Load Requirements: Accurately determine the torque and power requirements of the load. Use torque calculations and consider safety factors to ensure the gear motor can handle the demands of the application.
Efficiency: Energy efficiency is a key consideration, especially for machinery operating for extended periods. BLDC motors and AC induction motors with optimized designs offer higher efficiencies than DC motors.
Maintenance: Select gear motors that are easy to maintain and service. Look for designs with readily available spare parts and extended service intervals.
Cost: Balance performance requirements with budget constraints. Consider the total cost of ownership, including initial purchase price, maintenance costs, and energy consumption. MES-Drive offers a wide range of gear motors designed for various budgets and applications.

The integration of AI and IoT in agriculture is driving demand for more sophisticated and adaptable gear motor solutions. Future trends include:
Smart Gear Motors: Gear motors equipped with sensors and connectivity features that enable remote monitoring, diagnostics, and predictive maintenance. This allows for proactive maintenance and minimizes downtime.
Customized Gear Motors: Gear motors tailored to specific agricultural machinery applications, optimized for performance efficiency and longevity. MES-Drive is investing heavily in custom gearmotor solutions.
Energy-Efficient Designs: Continued advancements in motor and gear technology will lead to even more energy-efficient gear motors, reducing operating costs and carbon footprint.
Integration with VFDs: The increasing use of variable frequency drives (VFDs) allows for precise control of gear motor speed and torque, optimizing machine performance and energy consumption.
Gear motors are an indispensable component in agricultural machinery automation, and their selection directly impacts the efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of modern farming operations. By understanding the principles of gear motor operation and carefully matching them to specific application requirements, farmers can maximize the benefits of automation and increase productivity. The ongoing convergence of AI, IoT, and advanced gear motor technology promises to further revolutionize the agricultural sector, empowering farmers to optimize their operations and contribute to a more sustainable food supply. MES-Drive is committed to providing innovative and reliable gear motor solutions that are essential for powering the future of farming. As the agricultural industry embraces precision farming and data-driven approaches, the demand for high-performance, energy-efficient, and smart gear motors will only continue to grow.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked